Introduction
Every day, your team loses hours to the repetitive rituals that keep business moving—creating new project folders when contracts are signed, assigning tasks to team members based on workload, sending status updates to clients, calculating commissions when deals close, updating inventory after orders ship. These manual handoffs don't just waste time; they introduce errors, create delays, and turn your talented people into human copy-paste machines. When someone forgets a step or mistypes a number, projects start late, clients get confused, and fixing the mistake takes even more time. Meanwhile, your competitors deliver projects in days while you're still setting things up.
The Automation Engine transforms these friction points into seamless flows—signed contracts instantly spawn project templates and assign teams, completed milestones automatically notify clients, inventory adjusts itself after shipments, commissions calculate without spreadsheet formulas. It's about freeing your team from the mundane so they can focus on the meaningful, ensuring nothing falls through the cracks, and building a business that runs as fast as your market demands.
What is the Automation Engine?
The Automation Engine enables you to create automated workflows that connect your data, tools, and processes. Build visual workflows without code to eliminate manual tasks and ensure consistent execution.
Common use cases include sending notifications when data changes, creating tasks from form submissions, synchronizing data between systems, generating documents from templates, and processing bulk operations on schedules.
Getting Started
Accessing the Automation Engine
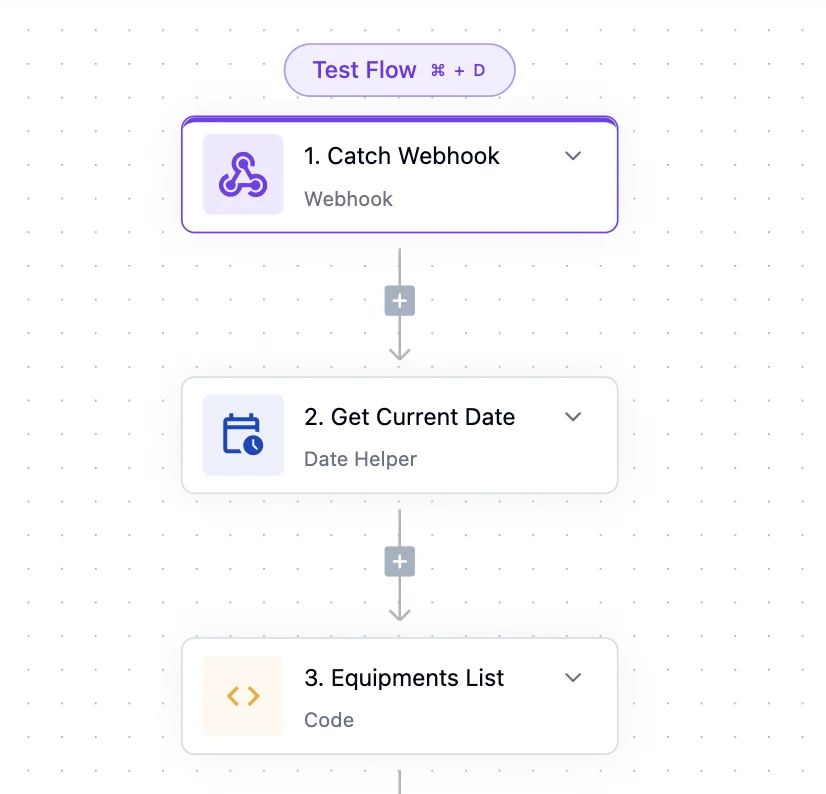
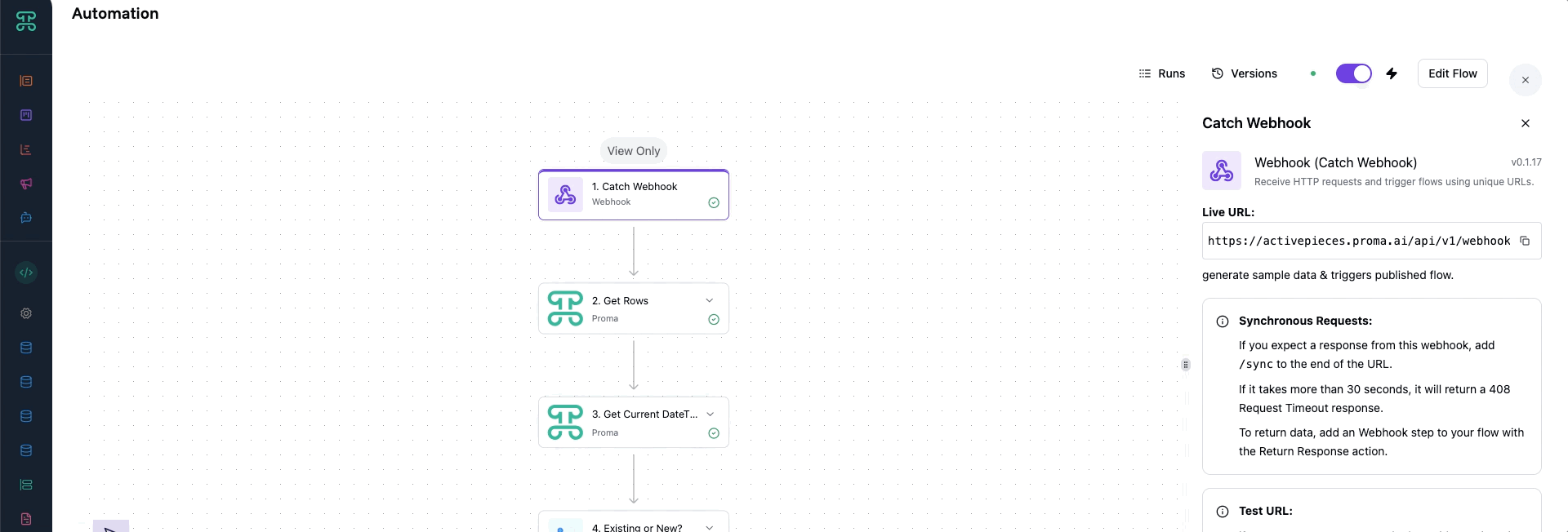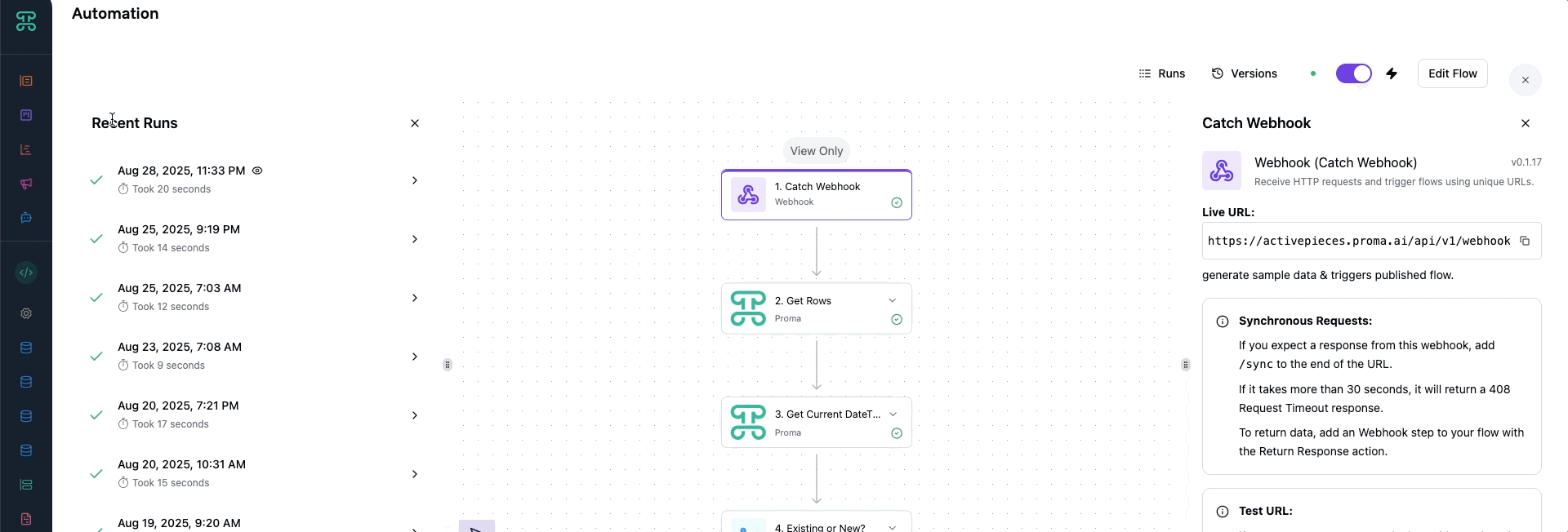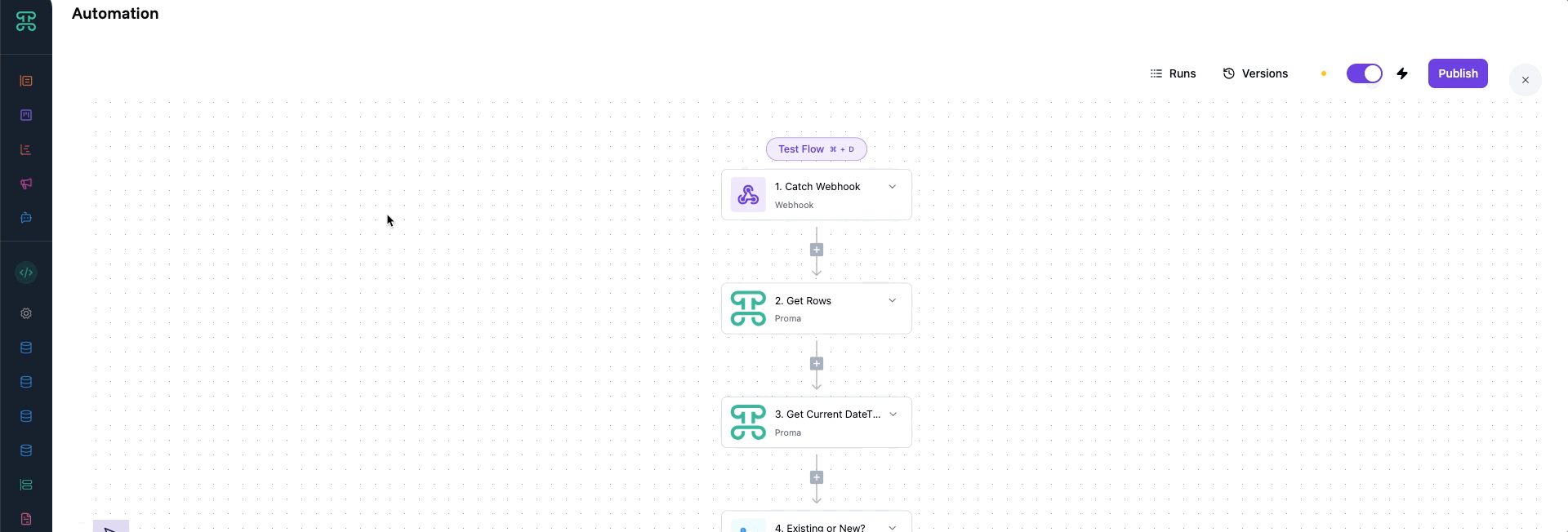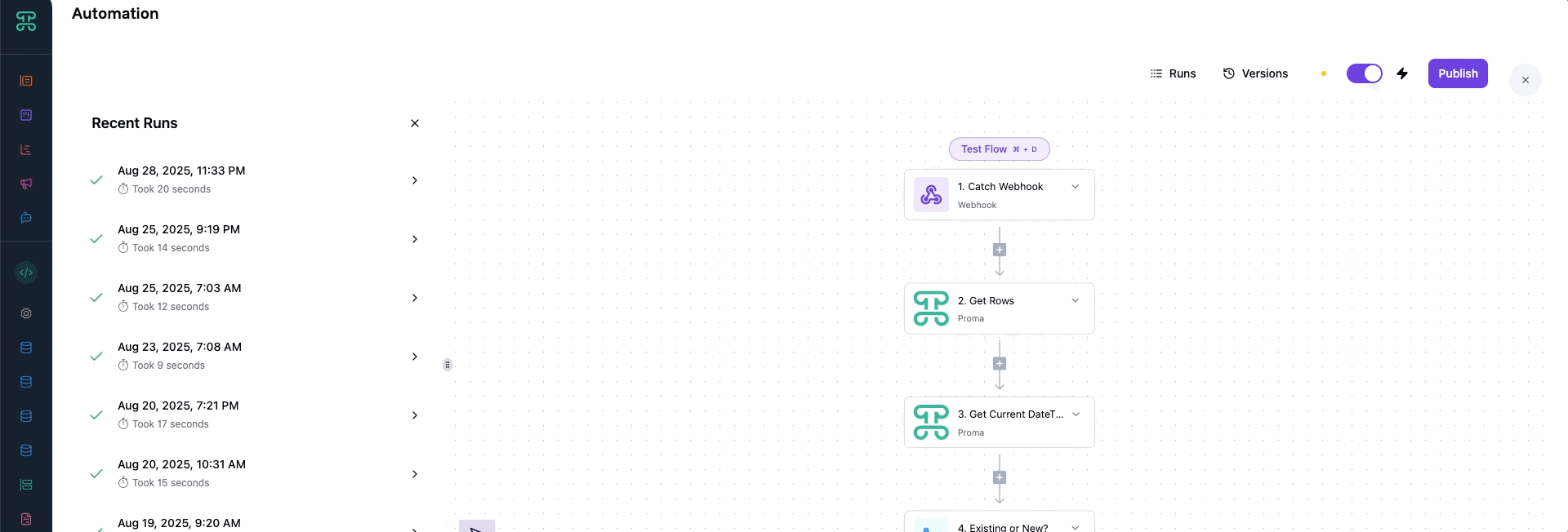
The path to automation begins in any Board within your workspace. Look for the "Build Mode" toggle in your left sidebar—this switches your Board from viewing to building. Once enabled, an "Automations" button appears, opening the visual workflow builder where you'll craft your automated processes.
The builder presents a canvas where you'll connect triggers to actions, creating flows that mirror your business logic. Here's how this looks in practice:

Core Components
1. Triggers
Every automation starts with a trigger—the spark that sets your workflow in motion. Proma provides four categories of triggers, each serving different automation needs.
Data Events
Your data is alive. Every time someone creates a record or updates a field, that's an event you can harness. Data triggers are the workhorses of most automations.
Insert Row fires the moment a new record enters your Dataset. Imagine a new lead appearing in your sales pipeline—this trigger could instantly assign it to the right salesperson based on territory and sends a welcome email.
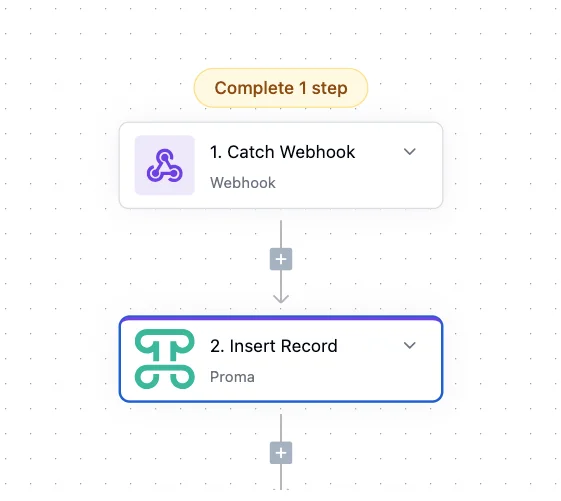
Updated Record responds to changes in existing records. This automatically notify a manager when any task gets updated.
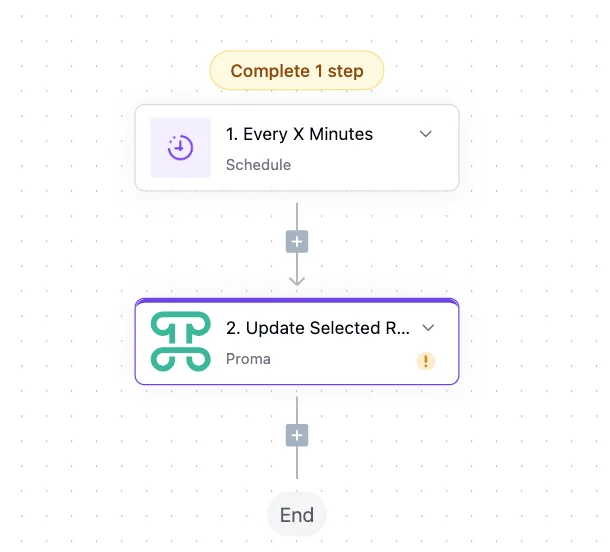
Update Selected Rows triggers when users perform bulk actions on multiple records simultaneously. Unlike single row updates, this trigger fires once for an entire selection, making it perfect for bulk operations like status changes, assignments, or archiving.
When a manager selects 20 tasks and marks them complete, Update Selected Rows passes all 20 record IDs to your automation. Process them efficiently in a single workflow—update time tracking, notify team members, adjust project progress, and log the bulk action. The trigger includes the user context, selected IDs, and the bulk action performed.
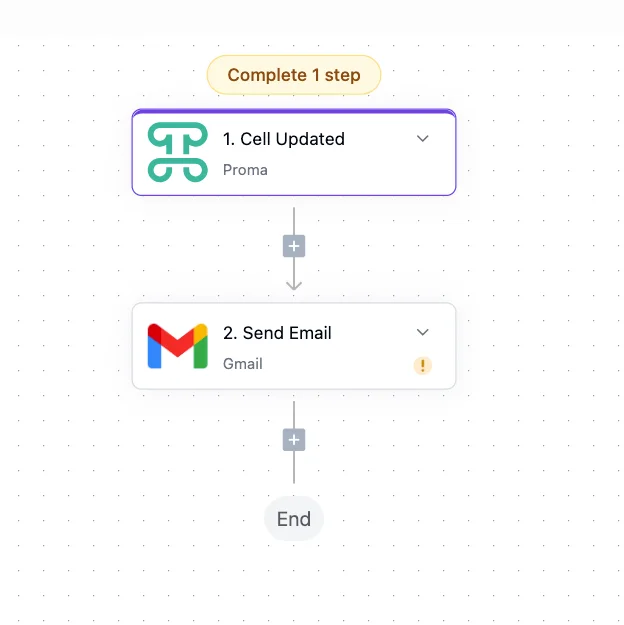
Cell Updated triggers when a specific cell value changes within a row. While Row Updated fires for any change in a record, Cell Updated provides granular control by monitoring individual fields. Perfect for workflows that should only activate when particular data points change—like triggering a credit check only when the loan amount field increases, or notifying a project manager only when the status column changes to "Blocked."
Enroll Fingerprint triggers during biometric registration processes. When employees or users register their fingerprint data for secure authentication, this trigger enables automated onboarding workflows—creating access profiles, assigning security clearances, sending confirmation emails, and updating HR systems. The trigger maintains security by passing only enrollment status and metadata, never the actual biometric data.
Fingerprint Event triggers when Proma's security system detects specific patterns or anomalies. This advanced trigger enables security-conscious workflows that respond to authentication events, access patterns, or potential security concerns.
Use Fingerprint Events to build automated security responses—logging unusual access patterns, triggering additional authentication requirements, or notifying administrators of potential issues. The trigger provides rich context about the event, including device fingerprints, location data, and behavioral patterns.
Configure sensitivity levels to balance security with user experience. High-sensitivity configurations might trigger multi-factor authentication for any new device, while standard configurations only respond to genuinely suspicious patterns.
Form Events
Forms are where your business meets the outside world. Form triggers ensure every submission receives immediate, appropriate attention.
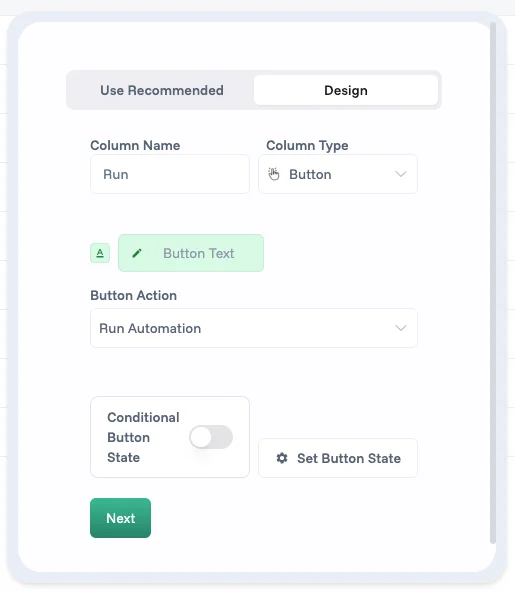
Run Automation activates when users click a Button column configured to trigger this automation. This puts control in your users' hands while maintaining consistency. Picture a "Generate Agreement" button on approved deals—one click pulls the latest terms, creates the contract, routes it for signature, and updates the deal status.
Scheduled Events
Not everything happens in response to user actions. Scheduled triggers bring time-based intelligence to your workflows.
Time-based triggers operate on simple schedules—hourly, daily, weekly, or monthly. Use these for regular maintenance tasks like archiving old records, sending digest emails, or generating reports.
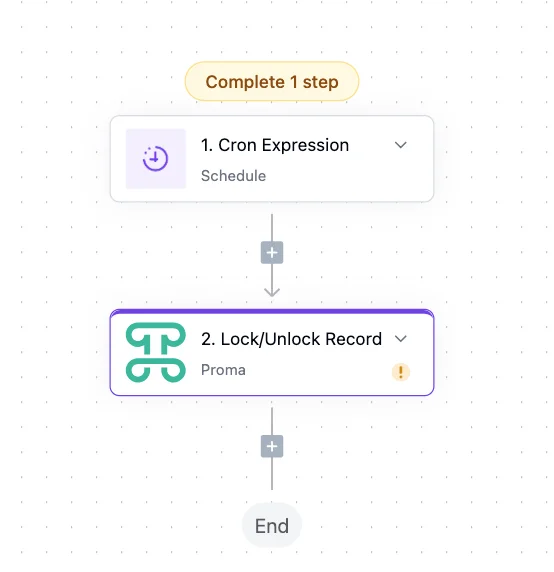
Cron Expression triggers offer precise timing control using the industry-standard cron syntax. Need something to run at 2:15 AM on the first Tuesday of each month? Cron expressions make it possible, perfect for complex scheduling requirements.
Start/Stop Timer triggers when users interact with time tracking columns. These events capture precise work duration for billing, productivity analysis, or project management. Start Timer fires when tracking begins, enabling automations that set user status to "busy," block calendar time, or notify team members. Stop Timer triggers when tracking ends, calculating duration, updating timesheets, checking against estimates, and potentially triggering invoice generation for billable hours. Both events include the task context, user information, and timestamp data.
External Events
Your business doesn't exist in isolation. External triggers connect Proma to the wider world.
Webhook triggers listen for incoming HTTP requests at a unique URL. When your e-commerce platform processes an order, your shipping provider updates tracking information, or your monitoring service detects an issue, web hooks ensure Proma responds immediately.
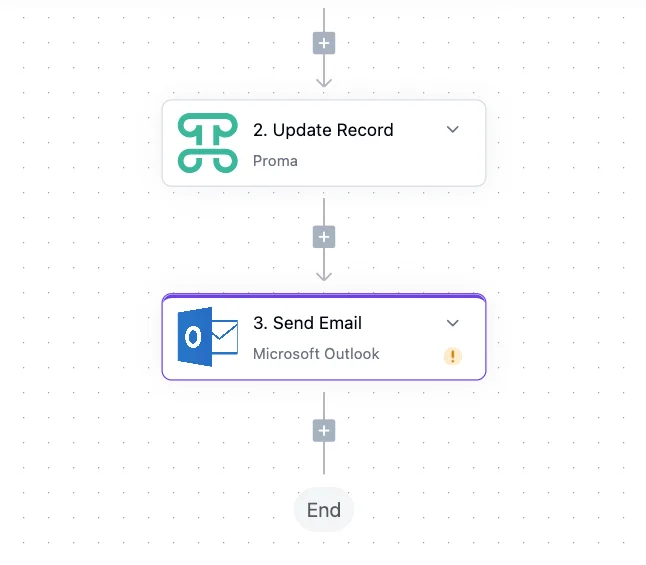
2. Actions
Actions are where automation delivers value. Each action represents a concrete step—sending an email, updating a record, calling an API. String them together to create sophisticated workflows that handle complex business processes.
Data Operations
At the heart of most automations lies data manipulation. These actions read, write, and transform information across your Datasets.
Insert Row adds new records to any Dataset in your system. When a support ticket arrives via email, this action might create the ticket record, populating fields with parsed email content and routing information.
Update Row modifies existing records, changing field values based on your workflow logic. Order shipped? Update the status. Payment received? Clear the outstanding balance. This action ensures your data always reflects current reality.
Delete Row removes records when they're no longer needed. Perhaps you're cleaning up test data, archiving old entries, or removing cancelled orders. Use with caution—deletions are permanent.
Warning: Delete Row actions are permanent and cannot be undone. Always test in a development environment first and consider archiving instead of deleting for audit trails.
Communications
Modern businesses run on communication. These actions ensure the right message reaches the right person at the right time.
Send Email sends email messages with conditional logic based on your workflow variables. The action supports rich templates where you can insert dynamic data—turning "Dear Customer" into "Dear Sarah Chen" with her recent order details. Configure sender addresses, reply-to settings, and even attachments generated by previous workflow steps. Configure conditions using the variable selector to determine email behavior. For example, only send if {{order.amount}} > 1000. The action evaluates conditions at runtime, ensuring emails are sent only when your business rules are met.
Proma AI Block
Integrates artificial intelligence capabilities directly into your workflows. This versatile action can analyze text sentiment, extract entities from unstructured data, generate content, classify information, or make intelligent routing decisions.
Configure the AI model, provide context, and specify output format. For example, analyze customer feedback to determine satisfaction scores, automatically categorize support tickets, or generate personalized responses based on customer history.
Format DateTime
Transforms date and time values between formats, timezones, and locales. Convert timestamps for international teams, format dates for documents, calculate business days, or prepare data for external systems with specific formatting requirements. Supports complex transformations like "next business day" or "end of quarter" calculations.
Get Current DateTime
Retrieves the current timestamp with timezone awareness. Essential for timestamping records, calculating durations, or scheduling future actions. Returns rich datetime objects that other actions can manipulate—add hours for SLA calculations, determine business hours, or check against cutoff times.
Proma JSON Stringify
Converts complex data structures into JSON strings for storage, transmission, or logging. Handles nested objects, arrays, and special data types gracefully. Use it to prepare data for webhooks, store configuration snapshots, or create audit logs with complete state information.
Proma JSON Extract
Parses JSON strings and extracts specific values using path notation. When webhooks deliver nested JSON payloads or APIs return complex responses, this action navigates the structure to retrieve exactly what you need. Supports JSONPath expressions for sophisticated extraction logic.
Proma Array Helper
Manipulates arrays with operations like filter, map, reduce, sort, and unique. Process bulk data efficiently—extract email addresses from user arrays, calculate totals from line items, find records matching criteria, or transform data structures for different systems.
Get Organization Info
Retrieves workspace metadata including organization name, plan details, user counts, and configuration settings. Use this for dynamic workflows that adapt based on your subscription level, generate branded content with organization details, or enforce limits based on plan restrictions.
Get Dataset Columns
Fetches schema information for any dataset in your workspace. Returns column names, types, and properties. Essential for dynamic automations that adapt to schema changes, validate data before processing, or generate documentation automatically.
Get Datasets
Lists all datasets accessible in your workspace with their metadata. Build dynamic workflows that discover available data sources, create cross-dataset reports, or validate references before processing. Includes permissions information to ensure automations respect access controls.
Get Spaces
Returns information about spaces (workspaces) available to the automation. Enable multi-workspace workflows, synchronize data across spaces, or build administrative tools that manage multiple environments. Includes space IDs, names, and access levels.
Invite User in Proma
Sends invitations for new users to join your Proma workspace. Configure role assignments, team memberships, and initial permissions. The action handles email delivery, tracks invitation status, and can trigger follow-up reminders for pending invitations. Perfect for automated onboarding when new employees are added to HR systems.
Update User in Proma
Modifies existing user profiles, permissions, and settings. Update roles when employees get promoted, adjust team assignments during reorganizations, or modify access levels based on training completion. The action maintains audit trails and can notify users of significant changes to their accounts.
Remove User in Proma
Handles user deactivation and removal workflows. When employees leave or contractors finish projects, this action ensures clean offboarding—revoking access, reassigning owned records, archiving user data, and updating directory systems. Configure whether to permanently delete or soft-delete for compliance requirements.
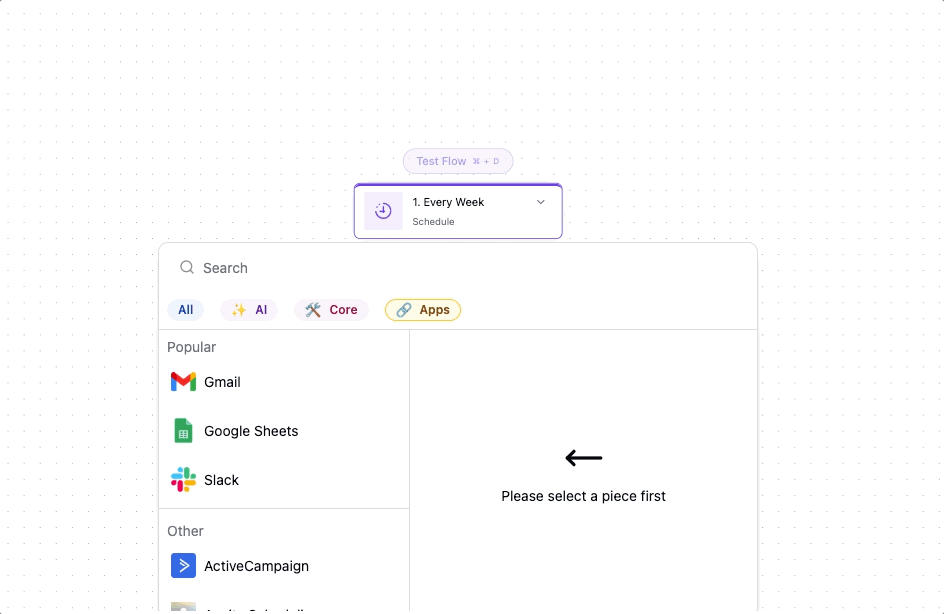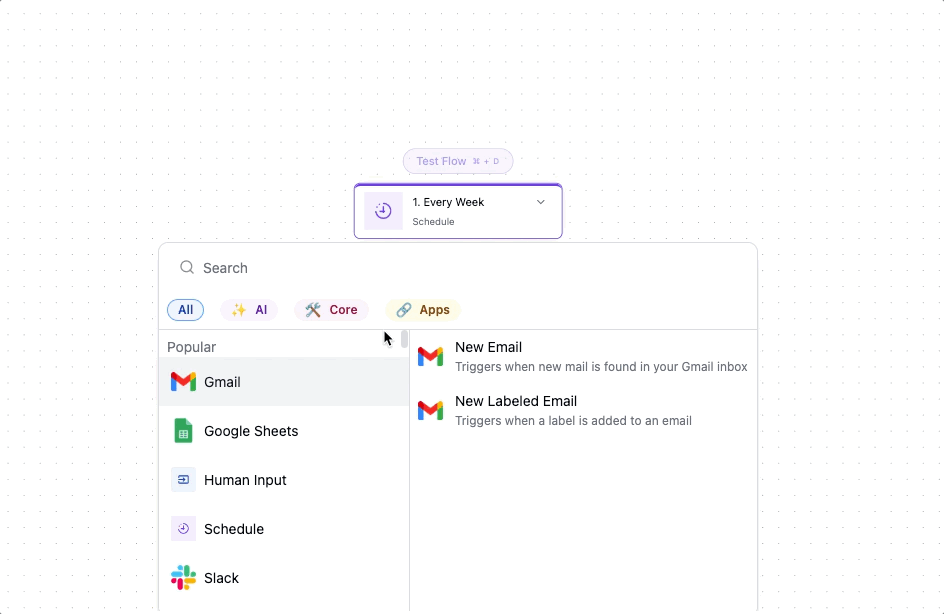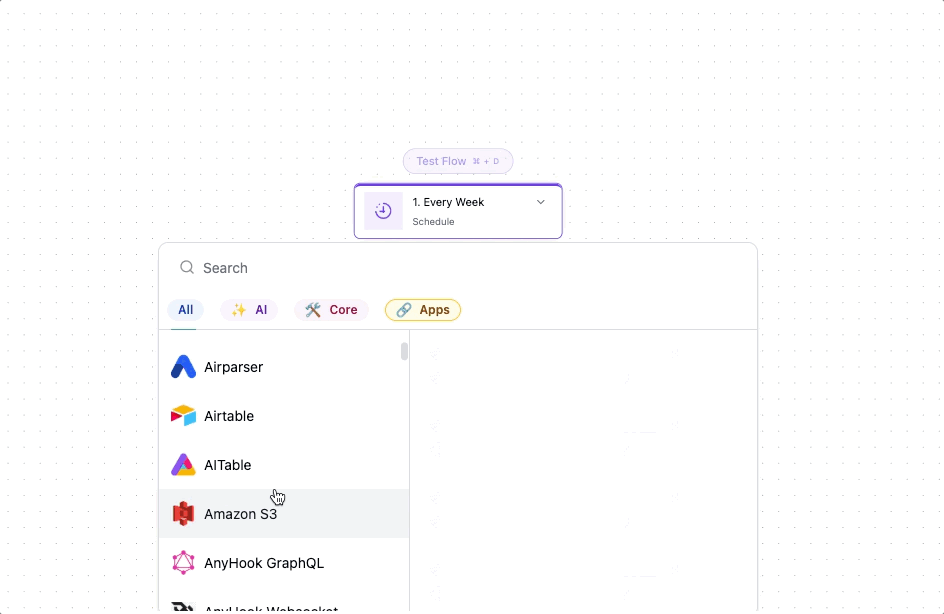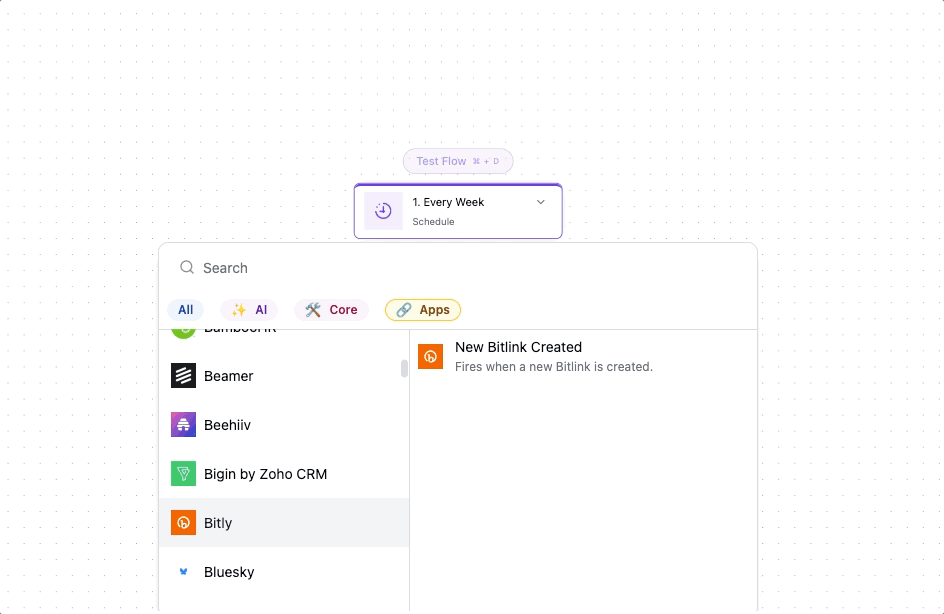
External Integrations
Proma lives at the center of your tech stack, orchestrating actions across all your tools.
The platform includes pre-built connectors for major business services. Google Workspace actions can create documents, update spreadsheets, and manage calendar events. Salesforce connectors synchronize customer data bidirectionally. Slack integrations keep teams informed through channel messages and direct notifications.
Each connector handles authentication, data formatting, and error recovery. You focus on what to do; Proma handles how to do it.
Advanced Operations
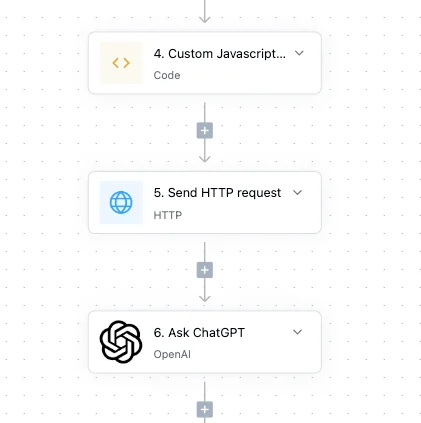
Sometimes you need capabilities beyond standard actions. These advanced operations unlock unlimited possibilities.
Execute JavaScript runs custom code within your workflow. Transform data in complex ways, implement business logic too nuanced for visual configuration, or integrate with services lacking pre-built connectors. The action provides a sandboxed environment with access to workflow data and common libraries.
Call API makes HTTP requests to any endpoint. Whether you're integrating with internal microservices, calling specialized APIs, or connecting to that one vendor who still doesn't have a proper integration, this action handles GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE requests with full header and authentication support.
AI Processing brings intelligence to your workflows. Generate content, classify text, extract information from unstructured data, or make decisions based on natural language inputs. The AI understands context from your workflow, producing relevant, accurate outputs.
3. Logic
Real-world processes rarely follow straight lines. Logic controls add intelligence to your automations, enabling them to make decisions and handle complexity.
Conditional Branching
Business logic often requires different actions based on circumstances. Logic controls turn your linear workflows into intelligent decision trees.
If/Else statements evaluate conditions and route execution accordingly. If the order total exceeds $1,000, send it for manual approval. Otherwise, process automatically. These binary decisions form the backbone of most conditional logic.
Switch statements handle multiple possibilities efficiently. Rather than chaining multiple If/Else blocks, Switch evaluates once and branches to the appropriate path. Perfect for routing support tickets by category or handling different payment methods.
Nested Conditions combine multiple logic levels. Perhaps high-value orders from new customers require extra verification, while repeat customers enjoy streamlined processing. Nest conditions to encode nuanced business rules.
Iteration
Many workflows process collections of data—all items in an order, every attendee in an event, each line in an uploaded file.
For Each loops process arrays item by item. When an order contains multiple products, loop through each one to check inventory, calculate shipping, and update quantities. The loop provides access to both the current item and its index.
While Loop continues until a condition becomes false. Use it for polling external systems, retrying failed operations, or processing queues of unknown length. Always include exit conditions to prevent infinite loops.
⚠️ Caution: Always include exit conditions in While loops to prevent infinite execution. Set a maximum iteration limit as a safety net.
Fixed Loop executes a specific number of times. Need to check something every hour for the next six hours? A fixed loop with a wait action handles it elegantly.
Flow Control
Not all actions should execute immediately or in sequence. Flow controls fine-tune your workflow's behavior.
Wait pauses execution for specified durations. After sending a welcome email, wait three days before sending the getting-started guide. Waits can be fixed (always 24 hours) or dynamic (until the scheduled appointment time).
Parallel Execution runs multiple action branches simultaneously. While one branch updates your CRM, another generates a PDF, and a third sends notifications. Parallel execution dramatically reduces total workflow time for independent operations.
Error Handling defines what happens when things go wrong. Network requests fail. APIs return errors. External services go down. Robust automations anticipate these failures, defining fallback actions that ensure critical processes complete even when individual steps fail.
Key Automation Features
Runs
Every automation execution creates a "run"—a complete record of what happened. Runs are your window into automation performance and behavior. The runs dashboard shows all executions at a glance.
Run Status Indicators:
✅ Success - Completed without errors
❌ Failed - Encountered error during execution
⏱️ Duration - Execution time in seconds
📋 Details - Full execution log
Track average execution times to identify bottlenecks. Monitor success rates to ensure reliability. Set up alerts for failure patterns that might indicate systematic issues.
Flow Toggle
The flow toggle acts as your automation's on/off switch, but with intelligence. When disabled, the automation preserves all configuration while ignoring triggers. This proves invaluable during maintenance windows, seasonal deactivations, or when debugging issues.
Consider a holiday promotion automation. Enable it during your campaign period, then disable it cleanly afterward. Next year, simply re-enable without rebuilding. The toggle maintains state without deleting valuable configuration work.
Real-Time Flow
Proma automations execute in real-time, processing triggers within milliseconds of occurrence. This speed enables responsive customer experiences and maintains data consistency across your system.
Real-time execution doesn't mean reckless speed. The engine manages queue depth, prevents cascade failures, and ensures reliable delivery even under high load. Built-in retry logic handles transient failures, while circuit breakers prevent systemic issues from spreading.
Versions
Professional automation requires version control. Every save creates a new version, preserving your automation's evolution over time.
The version history shows who made changes and when. Compare versions side-by-side to understand modifications. Roll back to previous versions if new changes introduce issues. Add commit messages explaining significant updates.
This safety net encourages experimentation. Try new approaches knowing you can always return to the proven version. Test major changes in development before promoting to production.
Automation Types
Proma provides three automation approaches for different use cases:
Standard Automations
Event-driven workflows that execute immediately when triggered.
Standard automations are your workhorses—event-driven workflows that execute immediately when triggered. They excel at responding to changes, processing submissions, and maintaining data consistency. Example is demonstrated in the building automation sections.
Consider a customer onboarding workflow. The moment someone completes your signup form, a standard automation springs into action. It creates their account record, sends a welcome email with login credentials, adds them to your newsletter, creates a getting-started task for your success team, and logs the acquisition in your analytics. All of this happens in seconds, automatically, every single time.
Building standard automations follows a predictable pattern. First, identify the triggering event—what kicks off this process? Next, map out the required actions in sequence. Configure each action with the necessary data mappings, pulling information from the trigger event or previous action results. Finally, activate the automation and monitor its performance. Also, another complete step-by-step example is demonstrated in the Building Automations section.
Automation Sequences
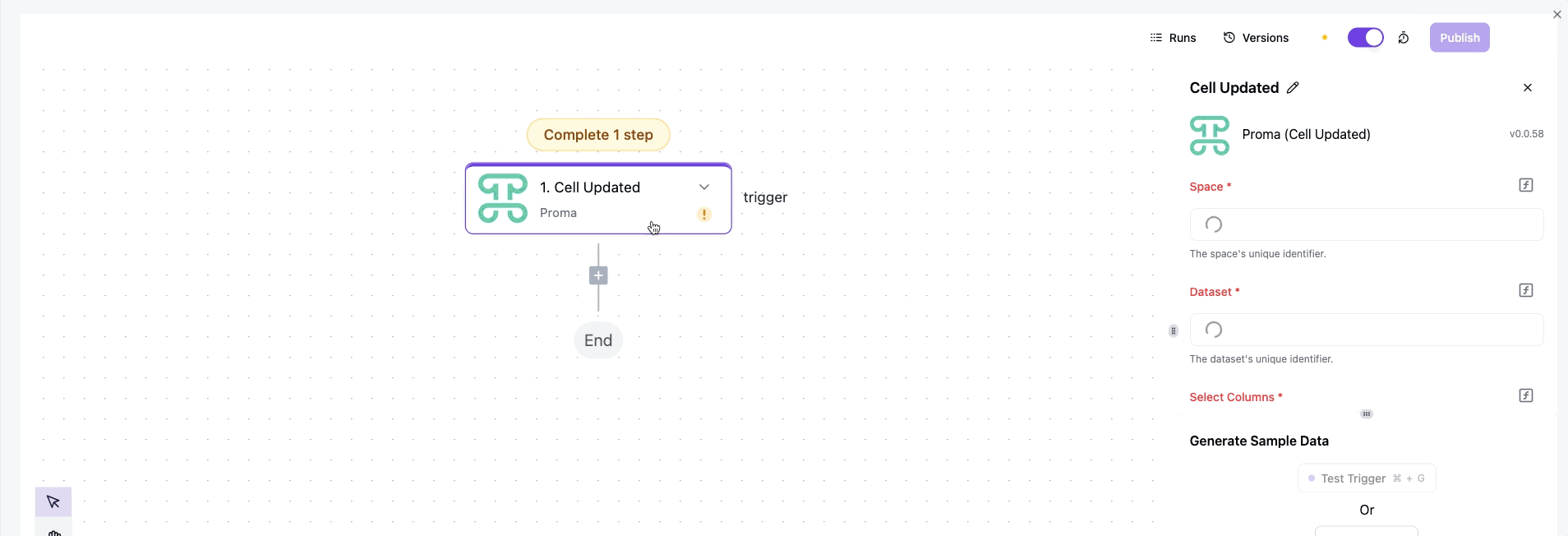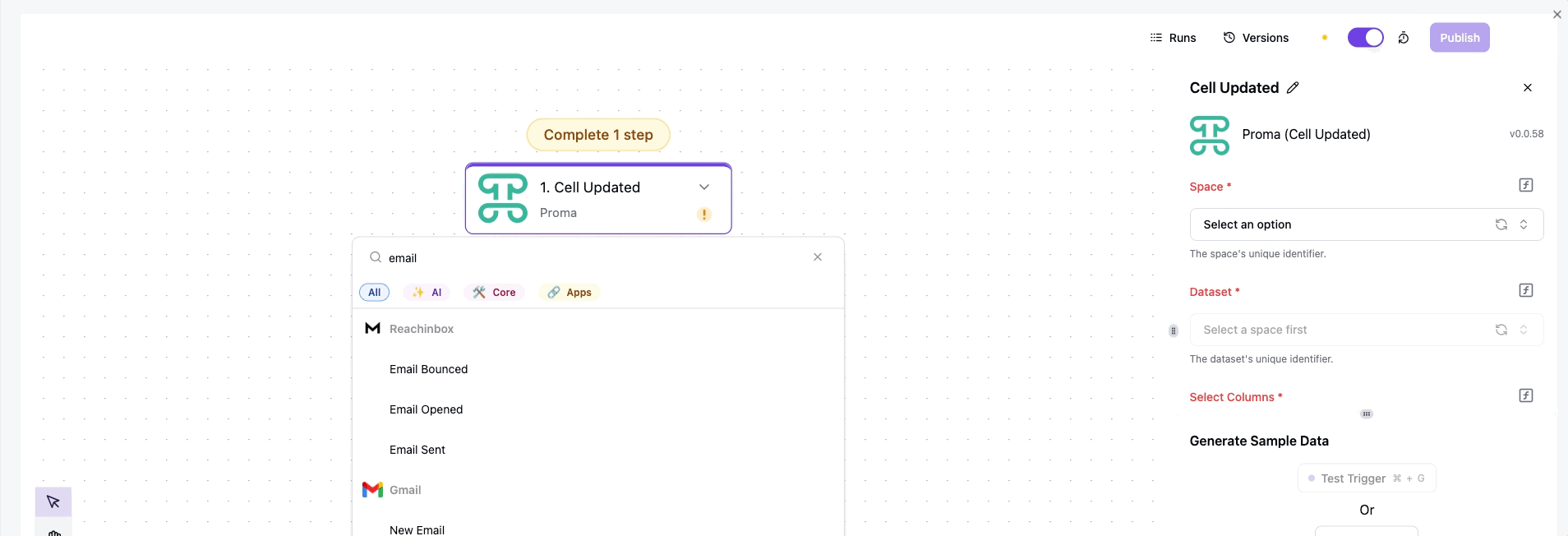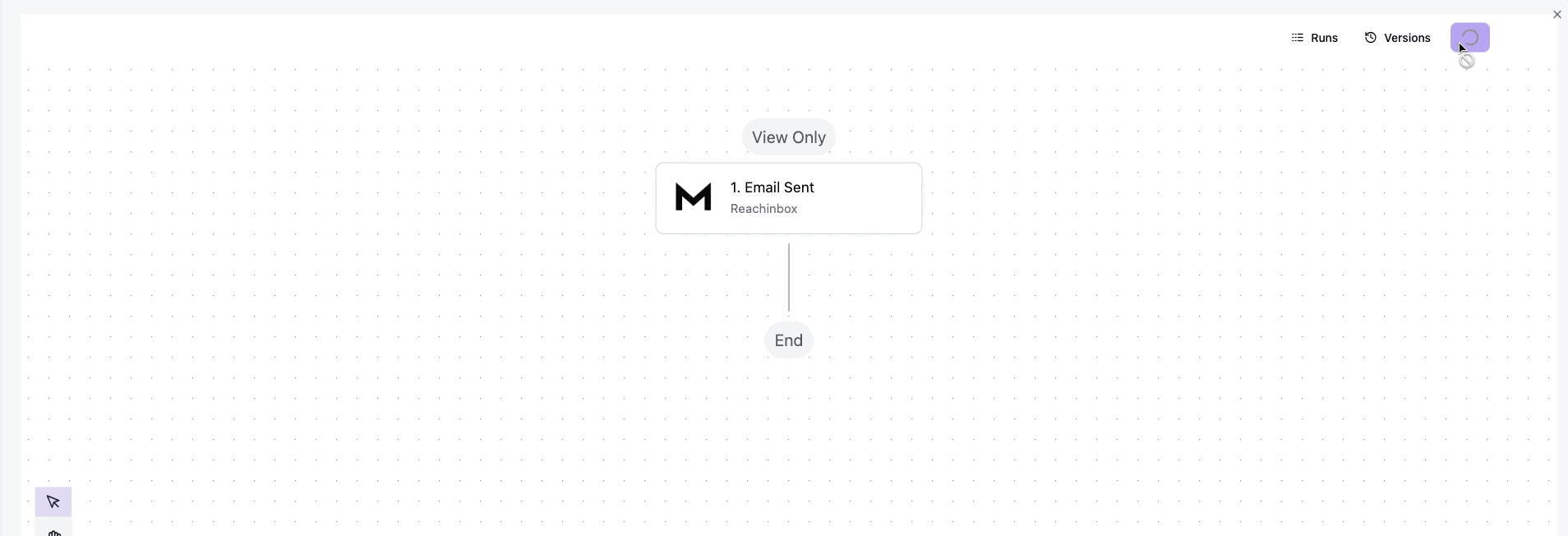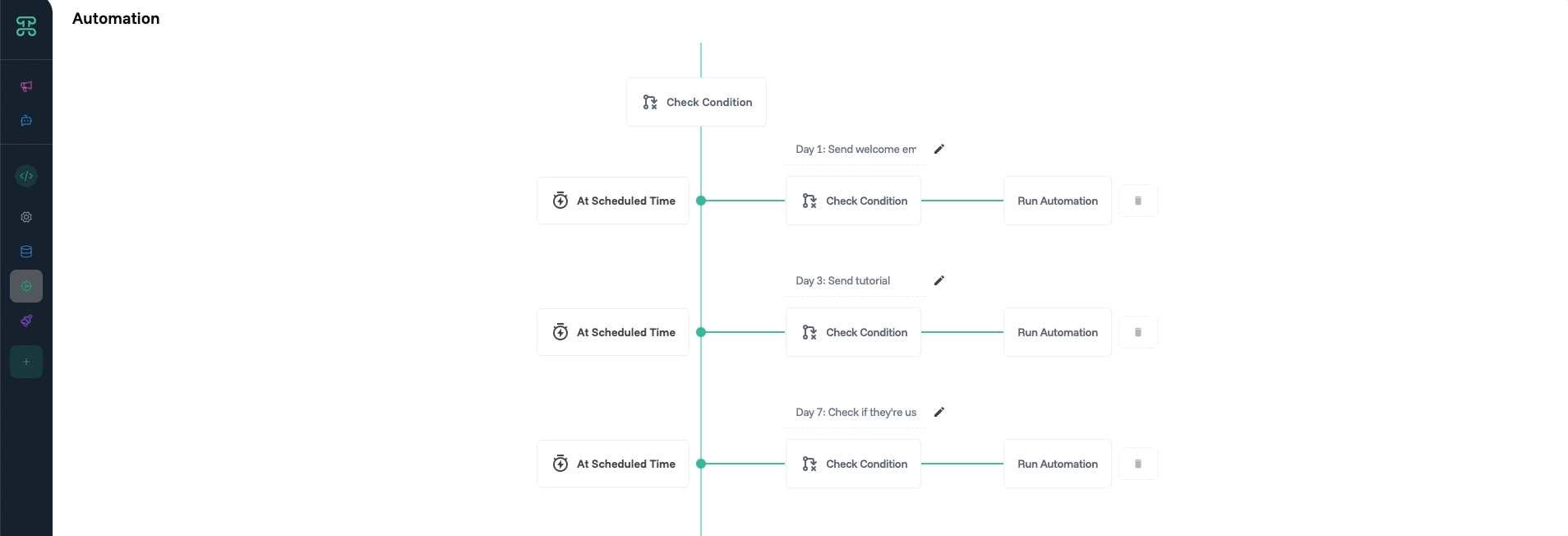
While standard automations excel at immediate responses, many business processes unfold over time. Automation sequences add temporal intelligence to your workflows.
A trial user nurture sequence demonstrates this perfectly. When someone starts a free trial, you don't want to bombard them with every possible resource immediately. Instead, a sequence delivers perfectly timed touch points. Day 1 brings a warm welcome and quick-start guide. Day 3 checks in with helpful tips based on their usage. Day 7 showcases advanced features they haven't discovered. Day 13 reminds them the trial ends soon, with a special offer to convert.
Sequences respect the natural rhythm of business relationships. They can pause when users take specific actions (no need to send "complete your profile" emails once they've done it) and resume when appropriate. Exit conditions ensure sequences end gracefully when their purpose is fulfilled.
In-Place Automations
Sometimes automation belongs right where users work. In-Place automations embed intelligent behavior directly into your data fields.
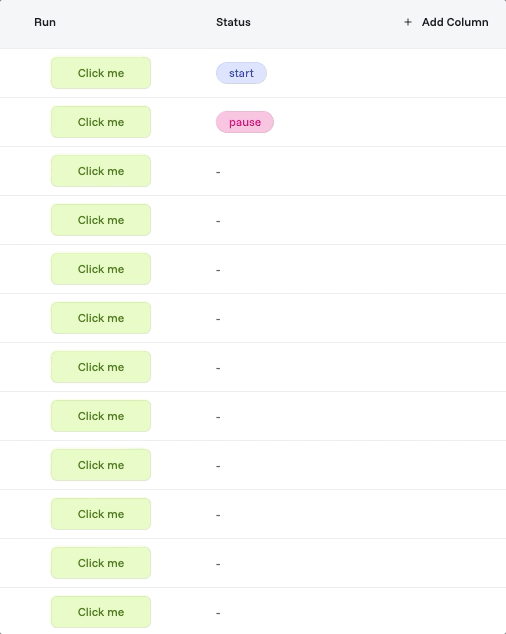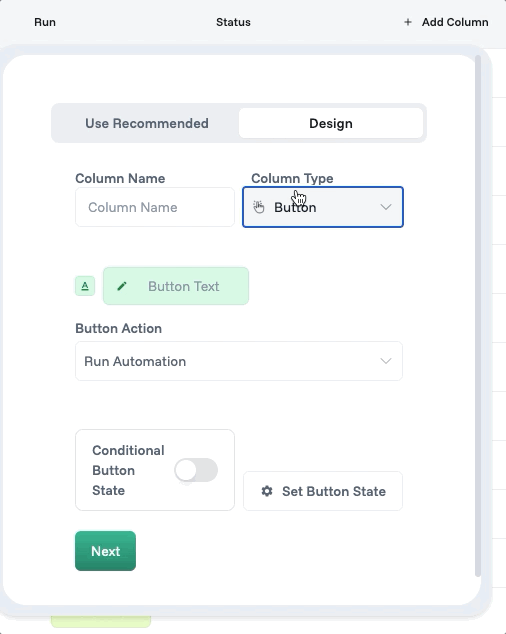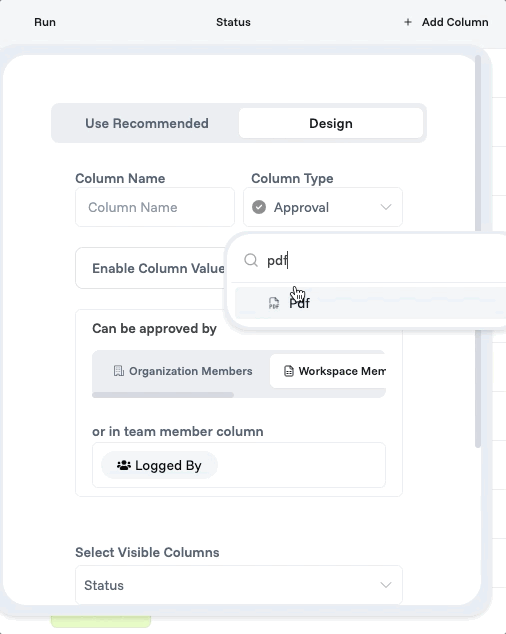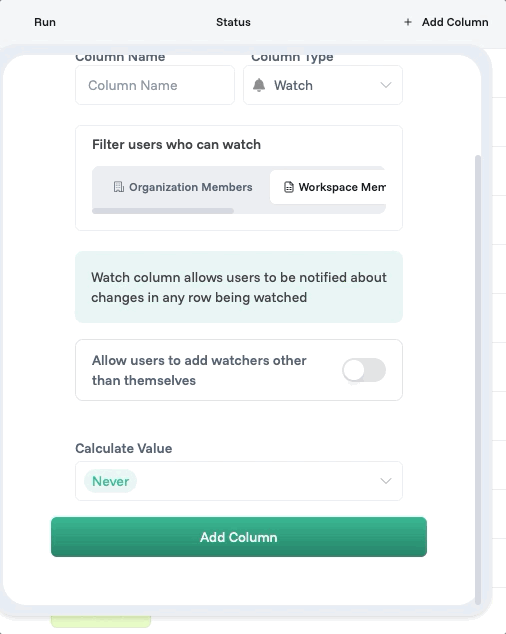
The Button column type transforms static data views into interactive command centers. Place a "Generate Invoice" button directly in your orders table. When clicked, it triggers an automation that pulls order data, generates a PDF, emails the customer, and updates the order status—all without leaving the current view.
Time Tracker columns automatically monitor duration. Team members click to start tracking time on a task. When they stop, the automation can update timesheets, calculate costs, and even trigger billing workflows for client work.
Approval columns embed entire approval workflows into a single field. The column shows pending/approved/rejected status with action buttons visible only to authorized approvers. Behind the scenes, automations route requests, send notifications, and enforce business rules.
Watch columns compute values based on other fields, but unlike simple formulas, they can trigger complex workflows. A "Calculate Shipping" field might call external APIs, apply business rules, and update multiple related records.
Document Generator columns create PDFs on demand. Click the field, and automation assembles data from across your system into professionally formatted documents using your templates.
You can find the columns when you click on “+ Add Column” button.
Building Automations
Create Your First Automation
Time to first automation: 5 minutes
This example creates an automation that sends an email when a form is submitted.
Enable Build Mode:
Open your Board → Toggle "Build Mode" → Click "Add Automations"
Set Your Trigger:
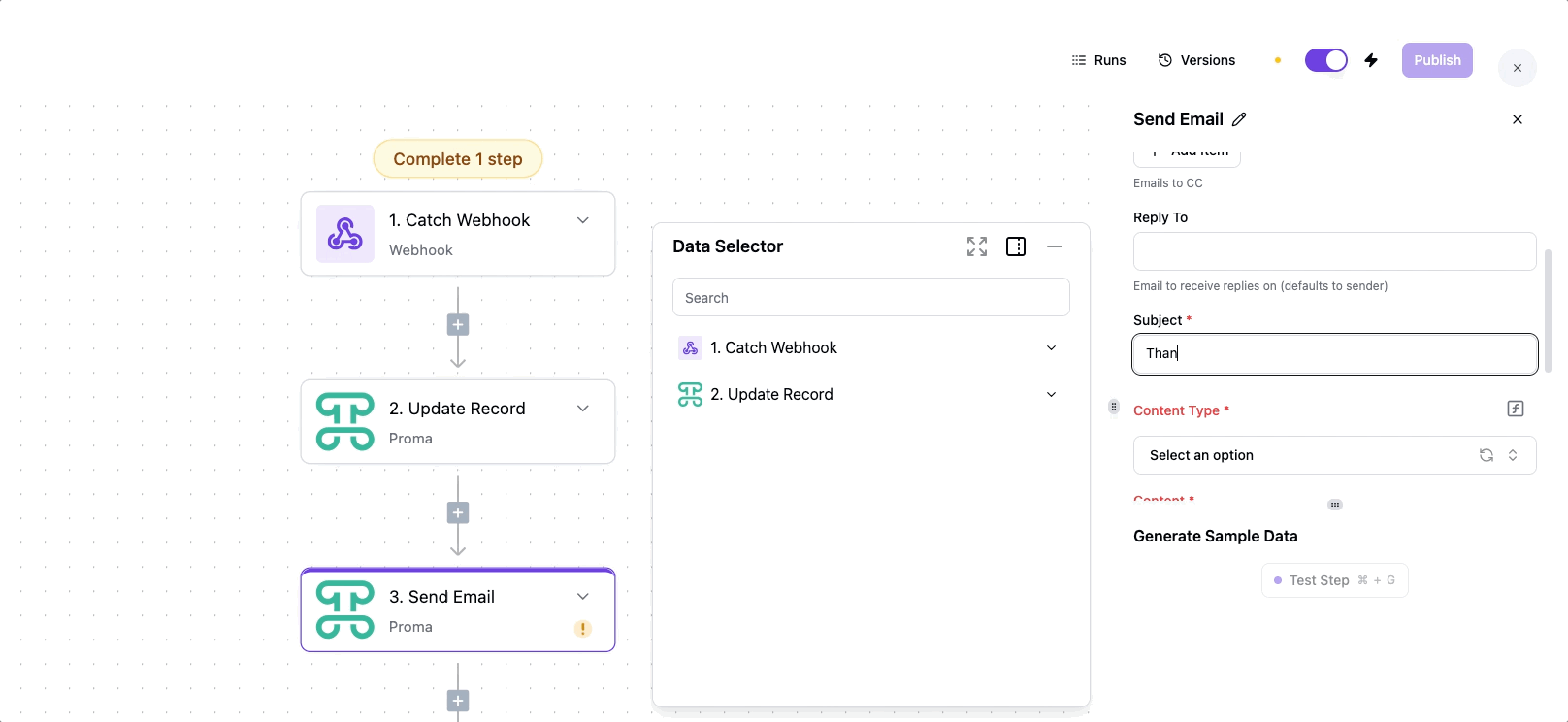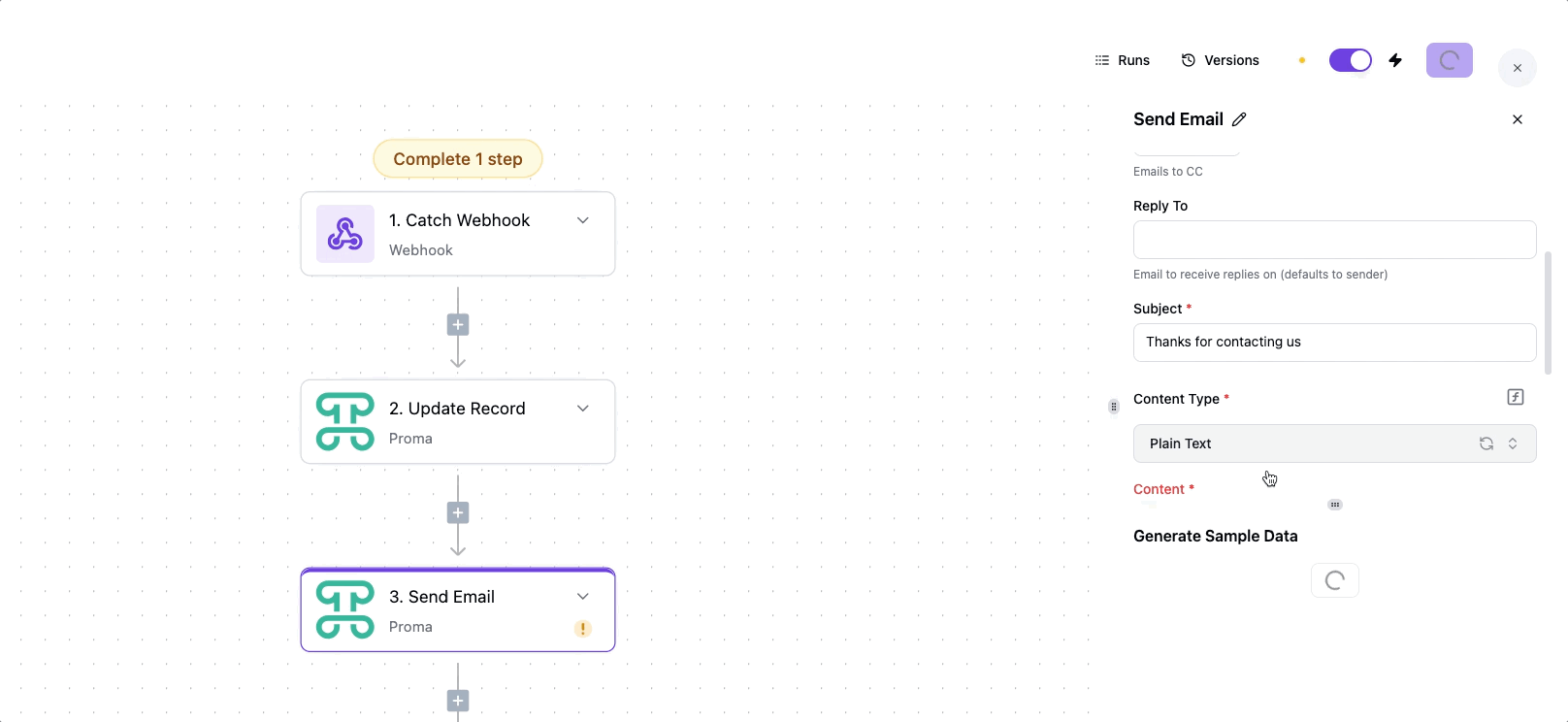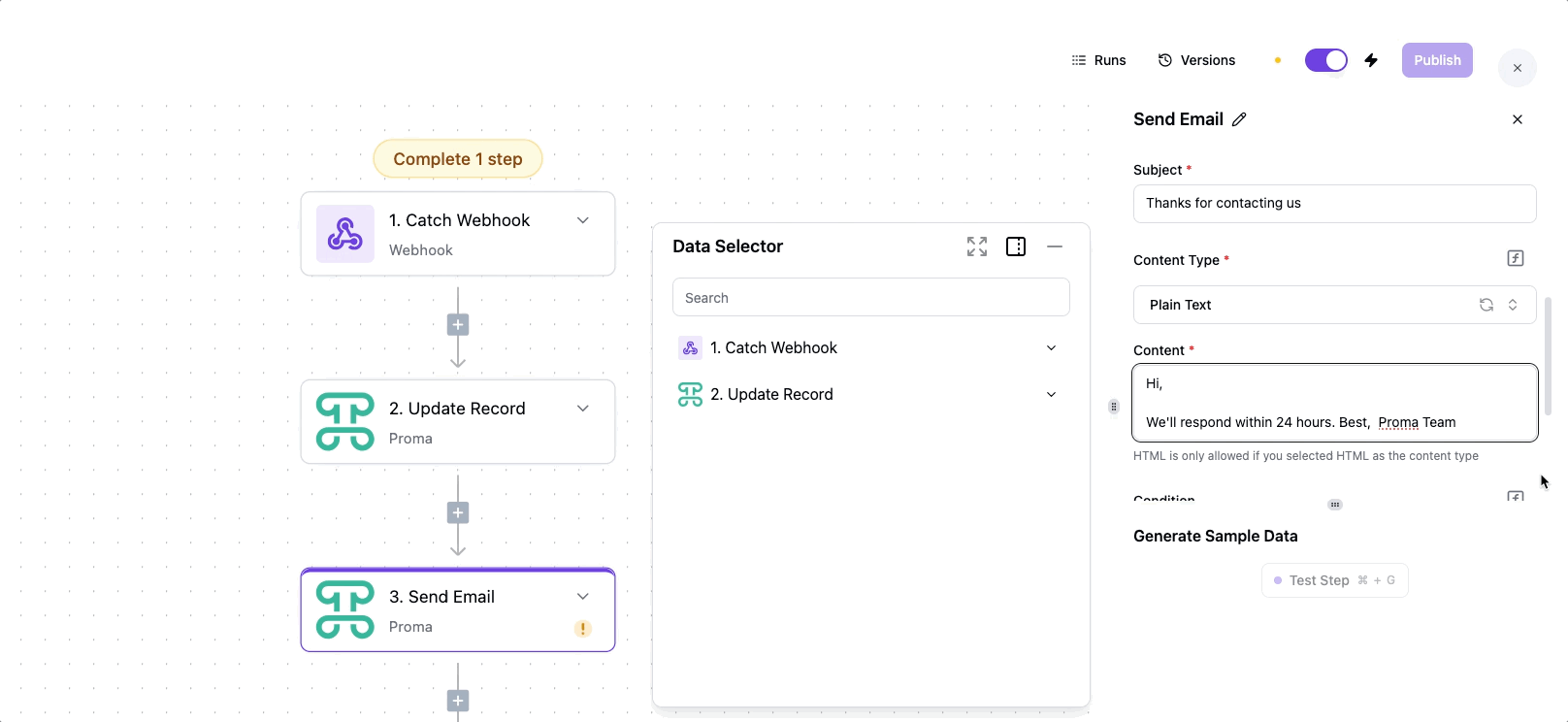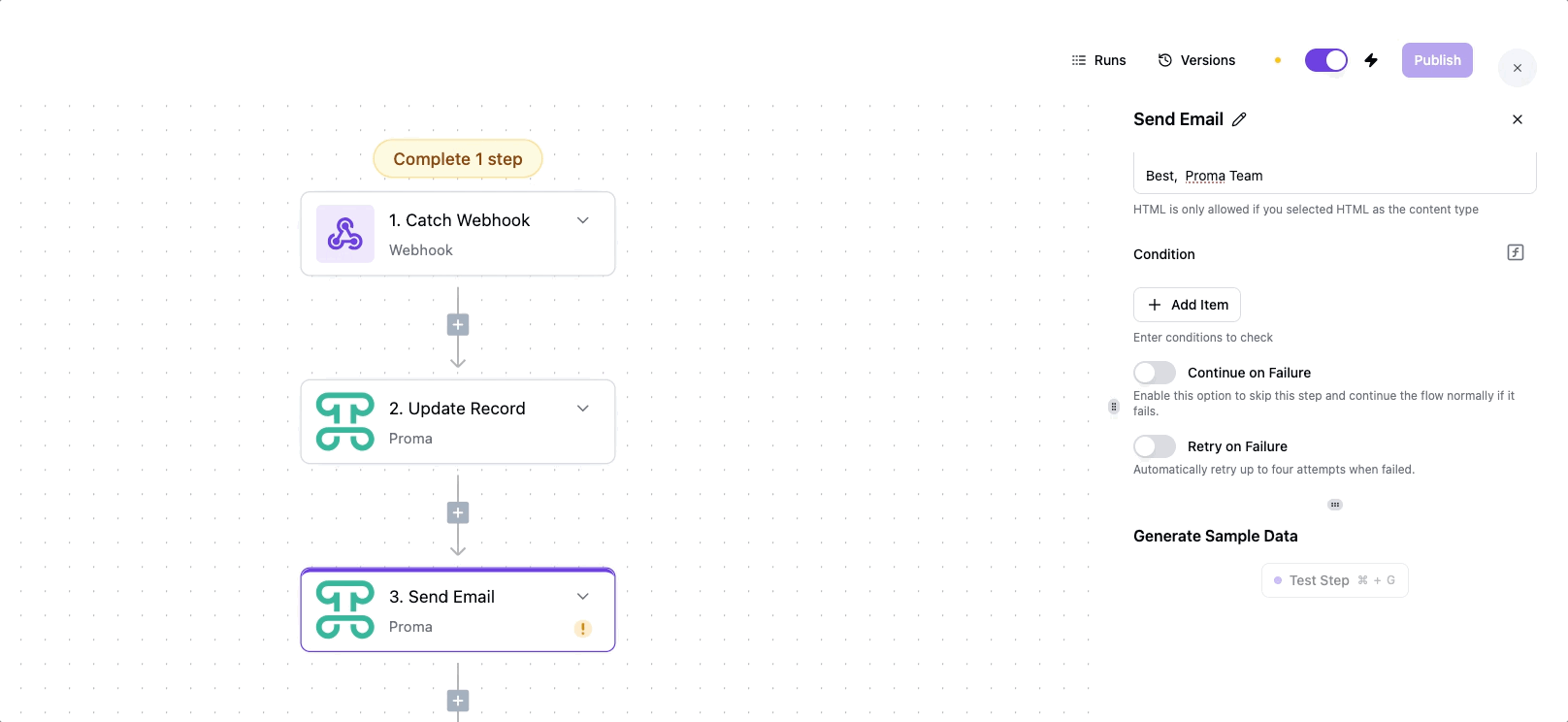
Name: "Welcome Email" Trigger: Form Submitted Select: Your contact form
Add Email Action:
Action: Send Email
To: Emails of the recipients
Subject: "Thanks for contacting us!"
Body:
Hi, We'll respond within 24 hours.
Best, Proma Team
Activate:
Save → Test with your email → Enable automation
✓ Done! Submit your form to see the automation in action.
💡 Pro Tip: Test automations with your own email address first. Create a dedicated test form to safely experiment without affecting live data.
Best Practices
Design Principles
Start Simple — Your first version doesn't need to handle every edge case. Build the core workflow that handles 80% of scenarios. Add complexity incrementally as you understand the process better and identify real-world requirements.
A customer onboarding automation might start by just creating an account and sending a welcome email. Once that works reliably, add user segmentation, personalized content, and multi-channel notifications.
Handle Errors Gracefully — Networks fail. APIs return unexpected responses. External services experience downtime. Robust automations anticipate these failures.
Wrap external service calls in error handlers. Define fallback actions for critical steps. Send notifications when manual intervention is needed. Log enough detail for debugging without exposing sensitive data.
Document Your Logic — Your future self (and teammates) will thank you for clear documentation. Use descriptive names for automations and actions. Add comments explaining complex conditions or business rules. Document external dependencies and their expected behaviors.
Performance Optimization
Batch When Possible — Instead of processing records individually, batch operations reduce overhead and improve throughput. If you need to update 100 records after a bulk import, a single batch update outperforms 100 individual updates.
Design workflows to accumulate changes and process them together. Use scheduled triggers to process queues periodically rather than immediately for non-urgent operations.
Minimize External Calls — Every API call adds latency and potential failure points. Cache frequently accessed external data. Combine multiple operations into single requests when APIs support it. Use webhooks to receive updates rather than polling for changes.
Optimize Loops — Loops require special attention. Process only necessary items by filtering datasets before iteration. Set reasonable limits to prevent runaway execution. Use parallel processing for independent iterations when the logic allows.
💡 Pro Tip: Schedule heavy batch operations between 2-5 AM when system load is lowest. Your automations will run faster and won't impact daytime users.
Security Considerations
Principle of Least Privilege — Automations should have exactly the permissions they need—no more, no less. Create dedicated service accounts for external integrations. Scope API keys to specific operations. Regularly audit and rotate credentials.
Protect Sensitive Data — Avoid logging personally identifiable information or authentication credentials. Use Proma's built-in secret management for API keys. Encrypt data in transit and at rest. Implement data retention policies that automatically clean up old logs.
Maintain Audit Trails — Every automation should leave breadcrumbs. Log significant actions and state changes. Include enough context to reconstruct what happened. Store logs securely with appropriate retention policies. Regular reviews help identify suspicious patterns early.
Troubleshooting
When Automations Don't Trigger
The most frustrating issue is an automation that simply doesn't run. Start by verifying the basics.
Check that the automation is enabled—it's easy to forget after testing. Confirm the trigger conditions match exactly what you expect. Field names are case-sensitive. Status values must match precisely. Date comparisons consider timezones.
Verify permissions allow the automation to access necessary resources. The executing user (often a service account) needs read access to trigger data and write access to any datasets being modified.
Review the trigger source specification. Ensure you've selected the correct form, dataset, or schedule. For webhook triggers, confirm the external service sends to the correct URL with expected data format.
Handling Execution Failures
When automations fail during execution, the run logs provide your investigation starting point.
Field name mismatches often cause failures when dataset schemas change. Someone renames "Customer Email" to "Email Address," breaking every automation expecting the old name. Regular schema audits prevent these issues.
Authentication failures manifest as 401 or 403 errors from external services. API keys expire. Passwords change. Service accounts get disabled. Implement monitoring for authentication failures and establish a credential rotation schedule.
Rate limiting causes sporadic failures during high-volume periods. External services protect themselves by limiting request frequency. Implement exponential backoff for retries. Consider caching to reduce API calls. Spread bulk operations across time to stay within limits.
Resolving Performance Problems
Slow automations frustrate users and can cascade into system-wide issues.
Large loops are common culprits. Processing thousands of records in a single automation can timeout. Break large operations into smaller batches. Use scheduled automations to process queues incrementally.
Sequential API calls create bottlenecks. If you're enriching records by calling an external service for each one, parallelize when possible. Batch APIs often provide better performance than individual calls.
Complex nested logic with many branches impacts performance. Simplify by breaking monolithic automations into smaller, focused workflows. Use lookup tables instead of long switch statements. Preach calculated fields over runtime computation.
Using Debug Mode
When standard troubleshooting fails, debug mode provides deeper visibility.
Enable debug mode in automation settings before running. Every action logs its input parameters, execution time, and complete output. Conditional branches show which path was taken and why. Loop iterations display their current index and item data.
Debug logs capture data at each workflow step, making it easy to identify where transformations go wrong. Compare actual values against expectations. Verify data types match—strings that look like numbers often cause subtle bugs.
Remember to disable debug mode after investigation. Debug logs consume more storage and can impact performance under high volume.
Next Steps
Explore related Proma features that enhance automation capabilities:
@Logic Builder - Create complex conditional workflows with visual programming
@Smart Columns - Add intelligent, automated fields to your datasets
@Interfaces - Build custom user interfaces that trigger and display automations
Have questions? Our team is ready to help at support@proma.ai